1. Setup BigQuery: Dataset and Table¶
The first step in any data pipeline is to prepare the destination. In our case, this is Google BigQuery. A Dataset in BigQuery is a container for your tables (like a database schema), and a Table holds your data in rows and columns.
Step 1: Create a BigQuery Dataset¶
-
Navigate to BigQuery Studio:
- In the Google Cloud Console, open the navigation menu (☰) and select BigQuery > Studio.
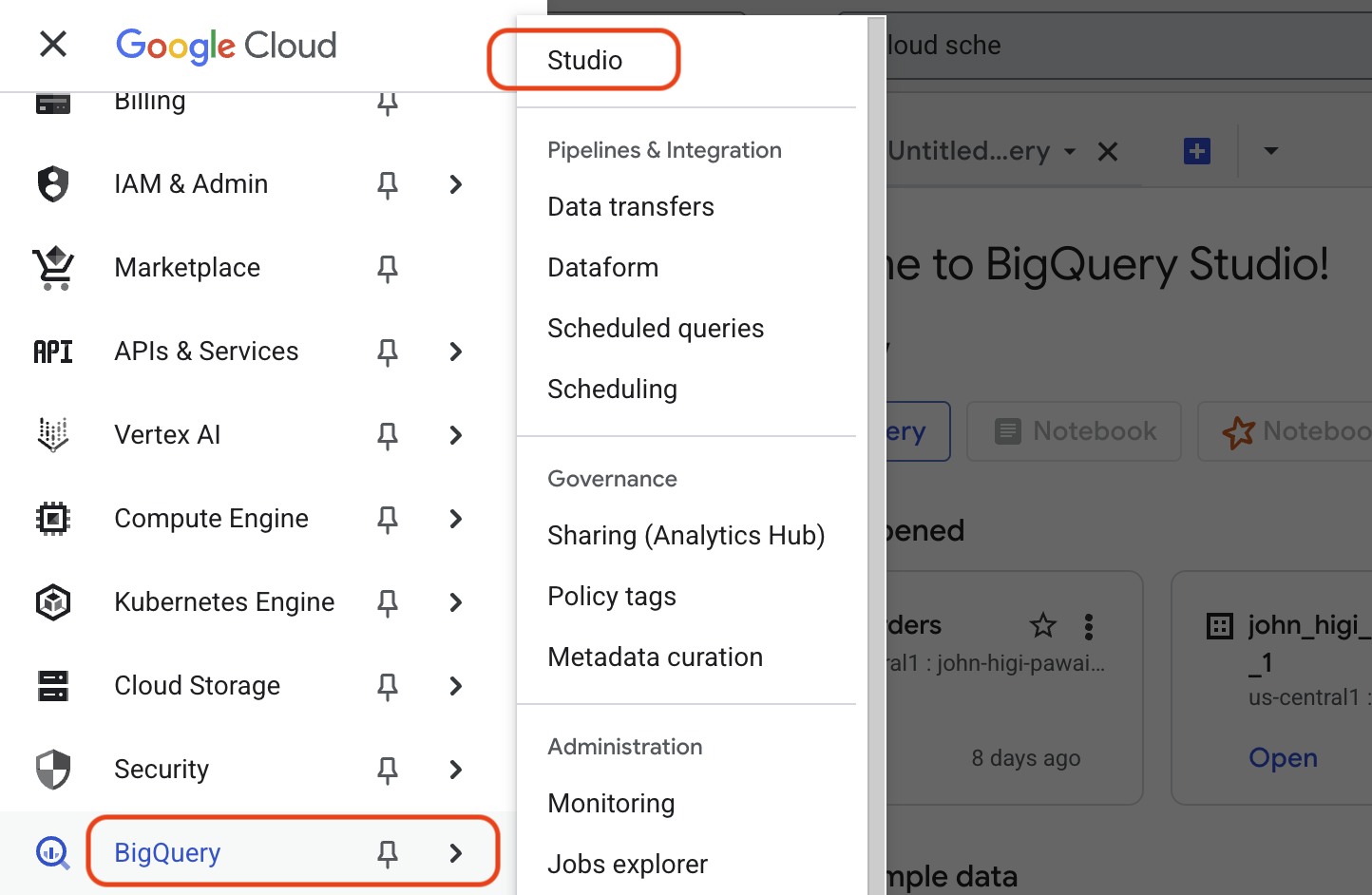
-
Initiate Dataset Creation:
- In the Explorer panel, click the three-dot menu (⋮) next to your project ID and select Create dataset.
-
Configure the Dataset:
- Dataset ID:
cloud_mastery - Data location:
us-central1(or your preferred region). !!! important You cannot change the location after creation. Choose a location close to your other services to optimize performance and cost. - Click CREATE DATASET. Your new dataset will now appear under your project in the Explorer panel.
- Dataset ID:
Step 2: Create a BigQuery Table¶
Now, let's create an empty table inside your dataset where the pipeline will load data.
-
Initiate Table Creation:
- In the Explorer panel, click the three-dot menu (⋮) next to your
cloud_masterydataset and select Create table.
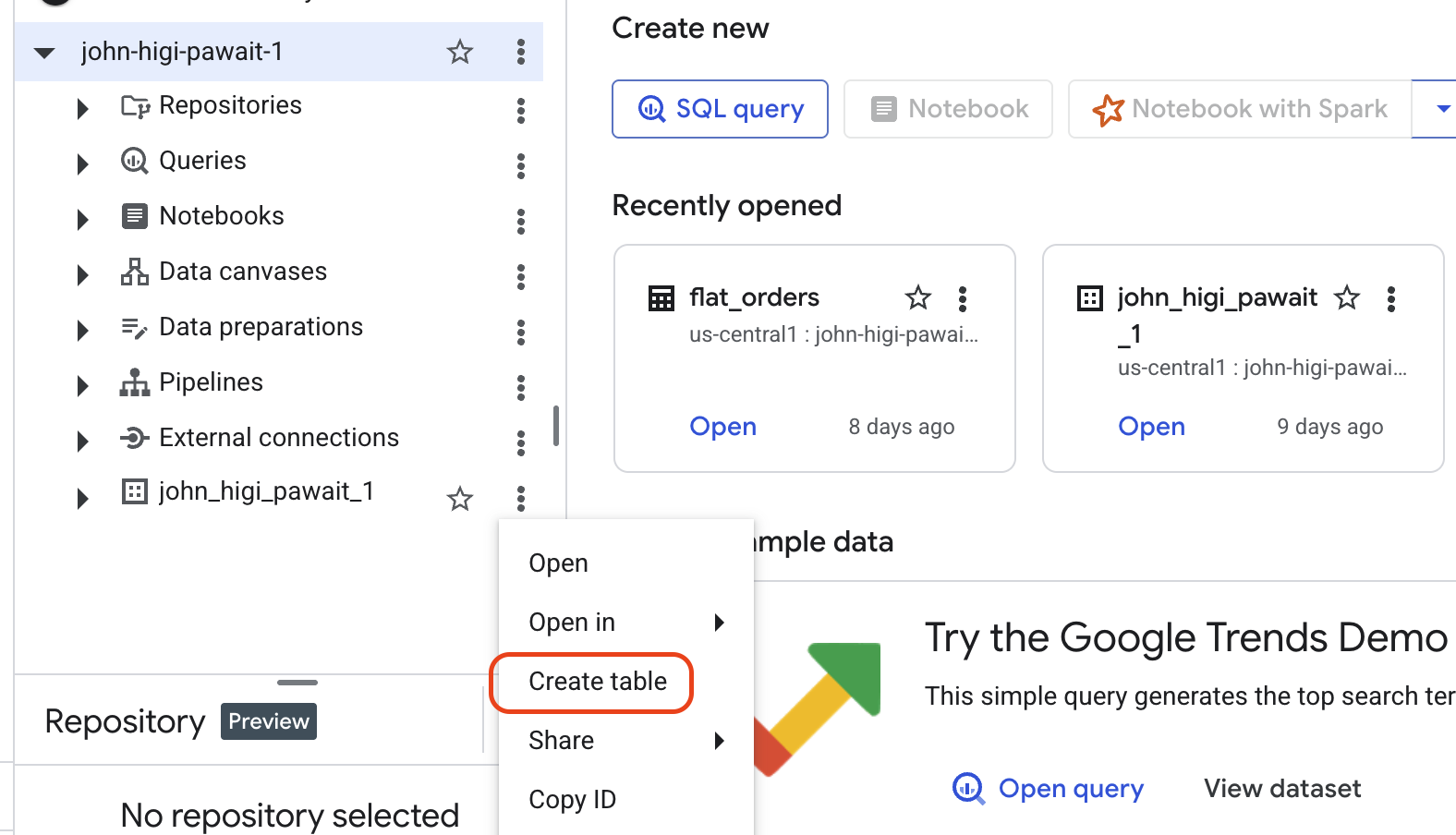
- In the Explorer panel, click the three-dot menu (⋮) next to your
-
Configure the Table:
- Source: Keep the default Empty table.
- Destination Table name:
denormalized_orders - Schema: Leave this blank for now. We will use BigQuery's
autodetectfeature when we load the data.
-
Click CREATE TABLE.
Your new empty table will now appear under its dataset. To view your table name, click on your table in the Explorer, then click on Details. Copy the Table ID for use in the next section.
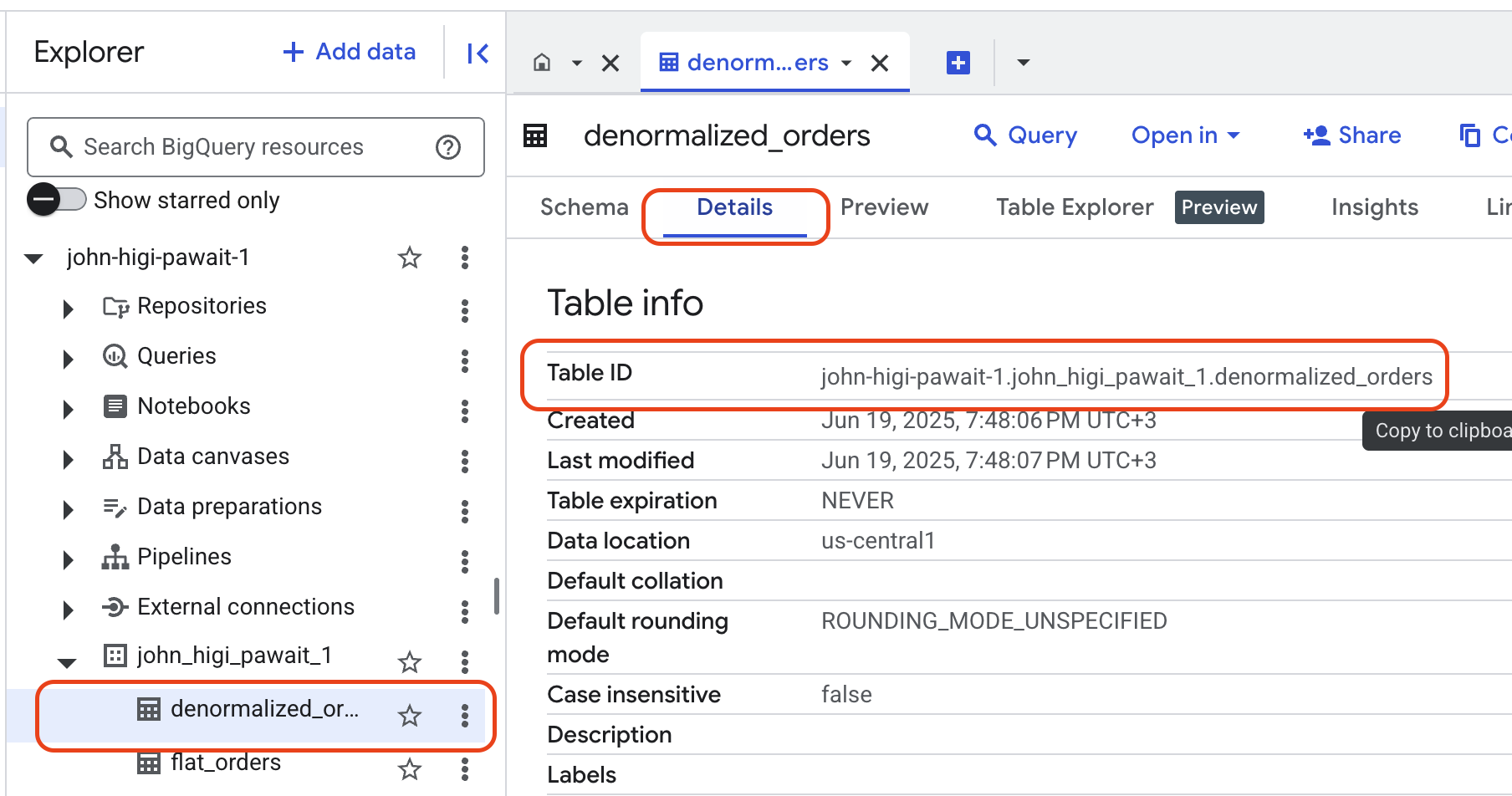
BigQuery Destination Ready
You have successfully created the dataset and table in BigQuery. This structure is now ready to receive data from our pipeline.
What's Next¶
With our destination ready, the next step is to build the core of our ETL process: the Cloud Function that will extract data from MySQL and load it into this table.